Patient Info
Eye Anatomy
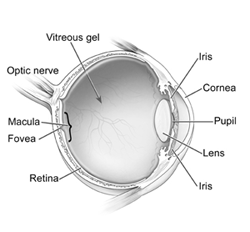
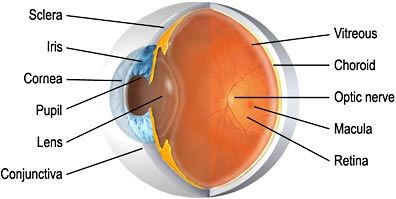
- The anterior chamber is the area bounded in front by the cornea and in back by the lens, and filled with aqueous
- The choroid , which carries blood vessels, is the inner coat between the sclera and the retina
- The conjunctiva is a clear membrane covering the white of the eye (sclera)
- The cornea is a clear, transparent portion of the outer coat of the eyeball through which light passes to the lens
- The iris gives our eyes color and it functions like the aperture on a camera, enlarging in dim light and contracting in bright light. The aperture itself is known as the pupil
- The lens helps to focus light on the retina
- The macula is a small area in the retina that provides our most central, acute vision
- The optic nerve conducts visual impulses to the brain from the retina
- The posterior chamber is the area behind the iris, but in front of the lens, that is filled with aqueous
- The pupil is the opening, or aperture, of the iris
- The retina is the innermost coat of the back of the eye, formed of light-sensitive nerve endings that carry the visual impulse to the optic nerve. The retina may be compared to the film of a camera
- The sclera is the white of the eye
- The vitreous is a transparent, colorless mass of soft, gelatinous material filling the eyeball behind the lens







